The other day, somebody asked me:
The other day, somebody asked me:
What is a business plan?
I think they were asking more than the obvious …
… I think they were really asking: “what makes a good business plan? what are the things I should include/ leave out?”
In any event, my answer was – and remains:
“A business plan is …”
A waste of time.
*Keep reading and I’ll tell you the only three times when you must write a business plan*
A very well-known guru once said of planning:
Four things can happen when you plan:
1. You plan and things turn out in your favor
2. You plan and things do not turn out in your favor
3. You do not plan plan and things turn out in your favor, anyway
4. You do not plan and things do not turn out in your favor
Of these, only 1. and 4. are as you expect …
… the rub is that the guru said that all 4 outcomes are equally likely.
In other words, there is no direct link with planning and outcome.
Mike Michalowicz, author of The Pumpkin Plan: A Simple Strategy to Grow A Remarkable Business In Any Field, agrees:
Financial projections for a new company are ludicrous. If we could project financials accurately for a public company for even one day, we’d be billionaires. How can we think we can project reliable financials for a company that doesn’t even exist?
Having worked (actually funded) close to 30 startup businesses to date, I wholeheartedly agree!
In fact …
… I have never written a business plan for any of my businesses.
But, I have used financial projections and written executive summaries for three specific purposes:
1. To impress people
I have used a short, one page ‘executive summary’ (like this one) to impress other people i.e. as a ‘sales tool’ for clients, bankers, and investors.
But, make no mistake, these are largely works of faction (fiction dressed as fact) i.e. to be used purely as marketing documents: proposals, marketing and sales presentations, and the like. Do not mistake them with documents actually intended to convince yourself of your business’ future success. For that purpose, I use the following two types of plans …
[AJC: The executive summary that I have shared with you has a place close to my heart: it was my first attempt at a purely online business as a founder/investor. We built the site, but never launched it. It was wonderful, overly ambitiously wonderful … the web equivalent of Howard Hughes’ Spruce Goose]
2. To check if my business is an opportunity worth pursuing
This type looks like the financial part of a business plan, but it’s not a plan, it’s actually a sanity-check:
I did this kind of financial plan (the kind that Mike says is “ludicrous” … and, I would usually agree) only once and you should do the same:
In 1998, I found my Life’s Purpose, and it sucked …
… for me, it meant lots of traveling and time not earning an income (basically, it meant very early retirement). It sucked because now that I knew what I really wanted to do with my Life, I could no longer just sit around and wait for it – and, my business – to ‘just happen’.
So, to passively fund the true cost of my new-found life (an expensive one!), I knew that I simply had to come up with $5 million dollars in just 5 years!
[AJC: for new readers, this is how I came up with the title of this blog, because I actually ended up making $7 million, but it took 7 years]
Now, there was just one small problem: in 1998, I was over $30,000 in debt!
So, I quickly realized that the only hope that I had of going from negative $30,000 to positive $5 million in 5 years was if I could make my business worth that much, quickly.
Working backwards, I asked around (i.e. my accountant and my friends who had their own businesses) to see what my business would need to ‘look like’ in order to be worth $5m to somebody else? The general consensus was that, as a private company if sold to a private seller, it would be worth around three to five times it’s annual taxable profit.
That means my business would need to generate $1m to $1.5 million in profit each year within 5 years …
… with only one small problem: it was currently losing money!
So, in comes the ‘business plan’:
All I wanted to know was: “was it even possible for my business to generate $1m to $1.5 million in profit each year?”
So I drew out a basic business plan (actually, financial forecast) with outrageously large sales growth (and, commensurate growth in expenses) to see: “at what annual sales volume (less reasonable expenses) will it be possible for my business to generate $1m to $1.5 million in profit each year?”
Once I found that revenue (i.e. sales or turnover) number, it was then relatively easy – again, with the help of a spreadsheet – to work out exactly how many customers that I would need, based on some guesses around the size and frequency of their average purchases and so on …
[AJC: now, I’m not even good with numbers and spreadsheets, but I didn’t even need my accountant to help me do any of this; but, if you need the help of yours, go ahead … it’s what they are there for!]
So, with the help of this ‘business plan’ (actually, the ‘financial forecast’ part of the business plan … but, it’s much the same thing), the question became a fairly simple one: ” can I find enough customers to make my business generate $1m to $1.5 million in profit each year?”
Sadly, the answer was: No.
My business would have needed each and every one of the Top 1,000 Corporations in Australia as my clients; given that I currently had 5, that was going to be a stretch [read: impossible] 🙁
So this form of business planning was for one reason and one reason only: to tell me if my business was an opportunity worth pursuing.
The answer, of course, was no … at least, not in it’s current form.
But, it pointed me to the right answer: which was to find markets that were much larger than Australia and relocate. Which we did … to Chicago … and, the rest is history.
[AJC: as it happens, I also had a financial epiphany, and realized that I should be investing – rather than spending – my businesses increasing profits, so a lot went back into the business, so that I could grow without needing to borrow or raise outside capital, but all of the remainder went into passive investments: stocks and real-estate. And, it’s these investments that took me to my first $7m in 7 years. Eventually selling my businesses was a huge dollop of cream on top!]
3. To check if the business can break-even
I do one other kind of business plan (again, I’m now just focussing on the financial forecast section … I never write the other 30 pages typical of most business plans): it’s the one that looks like a typical business forecast spreadsheet [you can download a copy of this example, here]:
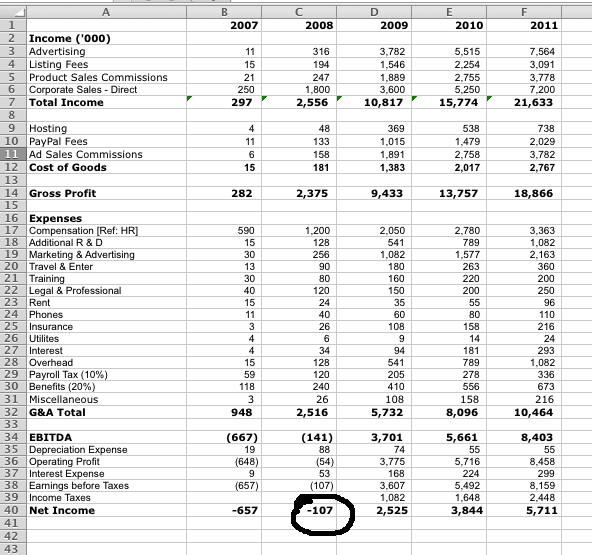
This one has a yearly projection of expected revenue growth, offset by expenses.
But, there’s only one thing that I’m looking for …
… it’s the column, where the bottom-line turns from red to black (actually, from negative to positive … from a loss to a profit)!
In fact, I’ll then fiddle with the numbers in that column to get the ‘bottom line’ number as close to $0.00 as possible (without being pedantic), because what I’m really trying to get a feel for is …
… the point where the business breaks-even.
[AJC: in this example, the 2008 column is closest to zero profit (showing a $107,000 loss), and just a few tweaks to the revenue and expenses quickly go that closer to $0.00, or break-even]
I do not care what Date the column says, that isn’t the point.
I do care what the numbers in that column look like:
– Does the sales number look achievable (i.e. for my business, is it more like 6 or 7 mid-size corporate customers than 1,000)?
– How many staff will I need? How big an office? Am I now going to bump into better funded competitors and have to try and steal all their customers, or is the market big enough for all of us?
– Will I need to expand interstate/internationally, franchise, and/or joint venture?
In other words, is it a business that I can comfortably take to break-even (before I run out of money)?
Why?
Well, once I know the business can break-even I know that I can then ride whatever storms come my way and take as long as I need to take to get my business to where it needs to be.
[HINT: see 2., above. Remember: even though I set my goal at $5m in 5 years, I actually took 7 years to make $5m plus a ‘bonus’ $2m]
So, don’t bother with a business plan, unless it’s for one of the three reasons that I outlined, above.
Now, tell me about your business plan successes and failures, so that mine don’t seem so lonely … 🙂
 This is quite typical of the types of questions that I receive from time to time:
This is quite typical of the types of questions that I receive from time to time: